The 10 m² area design is the only one which accommodate both the stall speed (without flaps) and cruise speed requirements from the specification. Another important requirement that can be checked from our analysis is if it can do a Paris-Stockholm trip.
Let's create a mission simulation:
- Click the 'Objectives' button in the navigation bar.
- Click 'New mission' on the left.
- Enter a mission name, 'Tutorial1-Paris-Stockholm' for example. Optionally, you can add a comment.
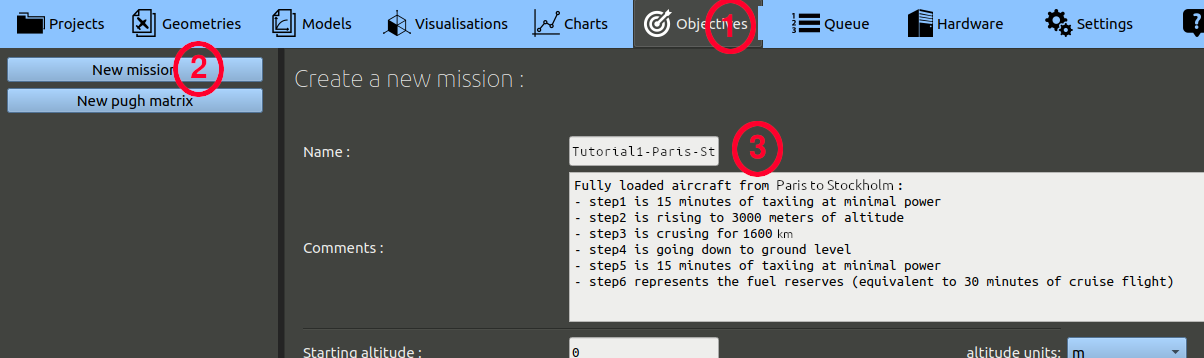
Next,
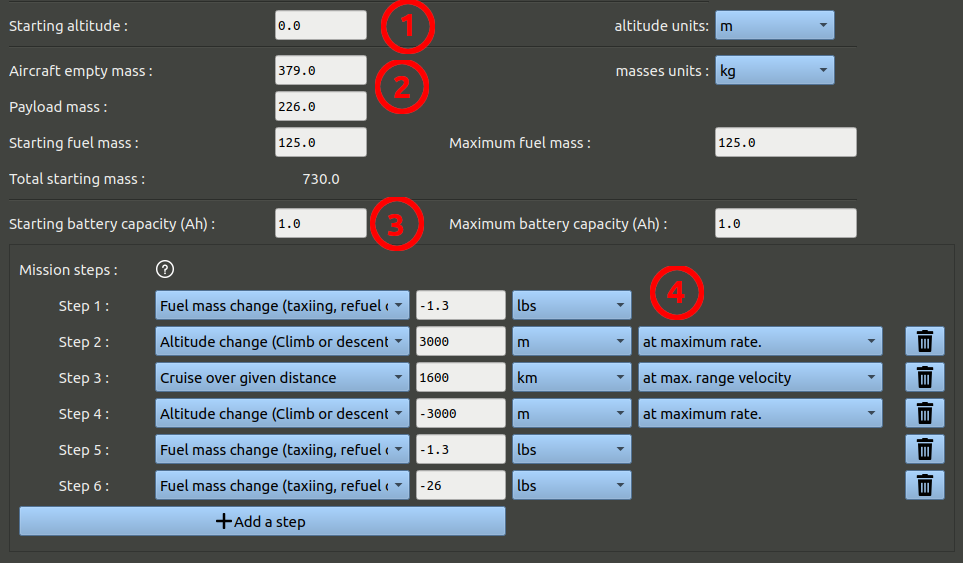
- Enter a starting altitude, 0m.
- Enter mass parameters.
- Enter 1 for battery capacity, we will not compute battery depletion in this example.
- Set up mission steps as shown in the image below:
- step 1 : Remove 1.3 lbs of fuel, this represent 15 minutes of taxiing at low power before take-off.
- step 2 : Gain 3000 meters of altitude (at maximum rate).
- step 3 : Cruise for 1600 km (at max. range velocity).
- step 4 : Loose 3000 meters of altitude (at maximum rate) to go down to ground level.
- step 5 : Remove 1.3 lbs of fuel, this represent 15 minutes of taxiing at low power after landing.
- step 6 : Remove 26 lbs of fuel, this represents the obligatory fuel reserves (equivalent to 30 minutes of flight in eco-cruise)
- Finally, click the 'Create' button.
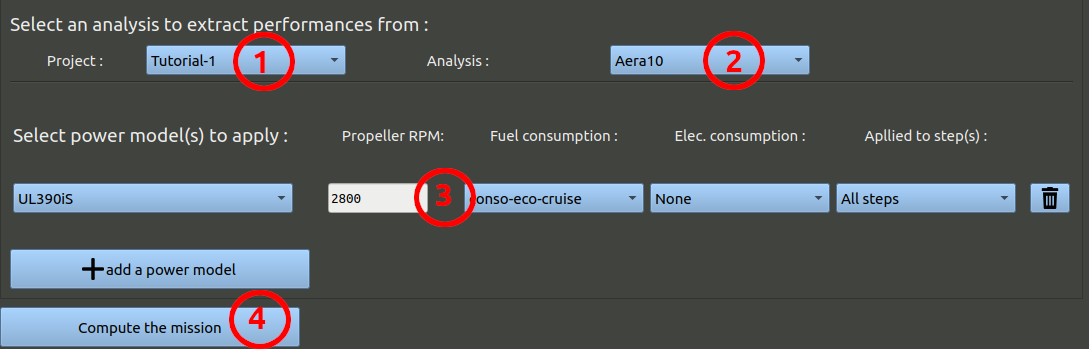
At the bottom of the mission, you can now select which analysis and parameters should be used to make the mission simulation.
- Make sure the right project is selected.
- Select the analysis corresponding to the 10 m² wing area.
- Add a power model, at 2800 RPM maximum (long duration cruise), with the fuel consumption model created earlier, but no electrical consumption model.
- Click 'Compute the mission'
A table will appear and show the mission's results. You should get a flight duration of less than 10 hours and an extra 26.5 lbs of fuel that could have been used to go farther or fly faster.
To conclude, the trip from Paris to Stockholm can be done without problem with the 10 m² wing area design.


